TCP/IP(Transfer Controle Protocol/Internet Protocol)
TCP/IP refers to Transmission Control Protocol/ Internet Protocol. Generally protocols are a set of instructions. TCP and IP were developed by a Department of Defense (DOD) research project to connect a number different networks (the “Internet”) .TCP is a transport layer protocol used by applications that require guaranteed delivery. It is a sliding window protocol that provides handling for both timeouts and retransmissions. The window size determines the number of bytes of data that can be sent before an acknowledgement from the receiver is necessary.
TCP establishes a full duplex virtual connection between two endpoints. Each endpoint is defined by an IP address and a TCP port number.
Sockets - is a name given to the package of subroutines that provide access to TCP/IP on most systems.
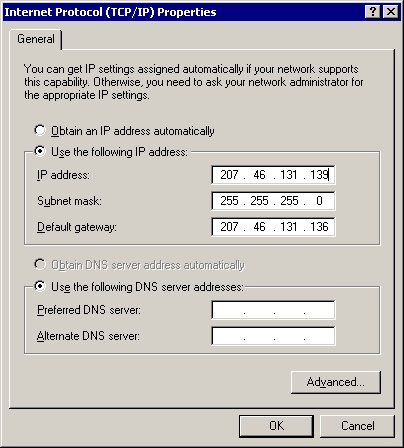
![]()
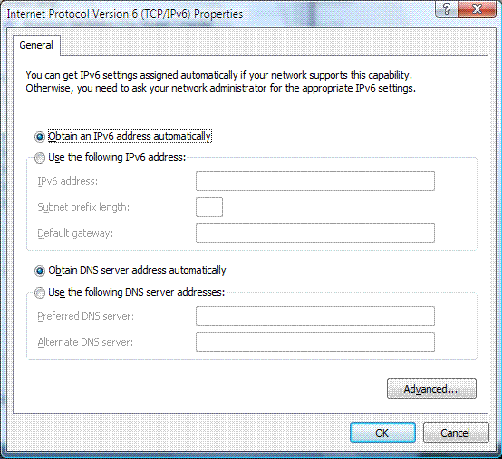
IPV6 in windows 7
IP - is responsible for moving packet of data from node to node. IP forwards each packet based on a four byte destination address (the IP number). The Internet authorities assign ranges of numbers to different organizations. The organizations assign groups of their numbers to departments. IP operates on gateway machines that move data from department to organization to region and then around the world.
IP has two versions which are IPV4 and IPV6
Now what is ipv4 and why is need of ipv6 ??
Limitations of IPV4
Scarcity of IPv4 Addresses: The IPv4 addressing system uses 32-bit address space. This 32-bit address space is further classified to usable A, B, and C classes. 32-bit address space allows for 4,294,967,296 IPv4 addresses, but the previous and current IPv4 address allocation practices limit the number of available public IPv4 addresses. Many addresses which are allocated to many companies were not used and this created scarcity of IPv4 addresses.
Solution of this problem NAT(Network address translation) is widely used.
Related : Difference (b/w) between IPV4 & IPV6 , Limitations Of IPV4


